The Garments manufacturing process is a fascinating journey that takes a basic concept and evolves it into a garment that can be purchased online or at stores. For designers, fashion brands, and consumers, understanding the stages of outfit creation is a fresh approach that brings actual value to one’s style.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through the detailed stages of the garments manufacturing process, from the initial sketch to the final packaged product. Whether you’re exploring the basics of apparel production or delving into the various types of garment manufacturing processes, this guide provides a comprehensive yet easy-to-follow overview.
Start to End Process of Manufacturing Apparel
Creating a piece of clothing is not just about stitching fabric together — it’s an orchestrated sequence of creativity, precision, and planning. Let’s break it down:
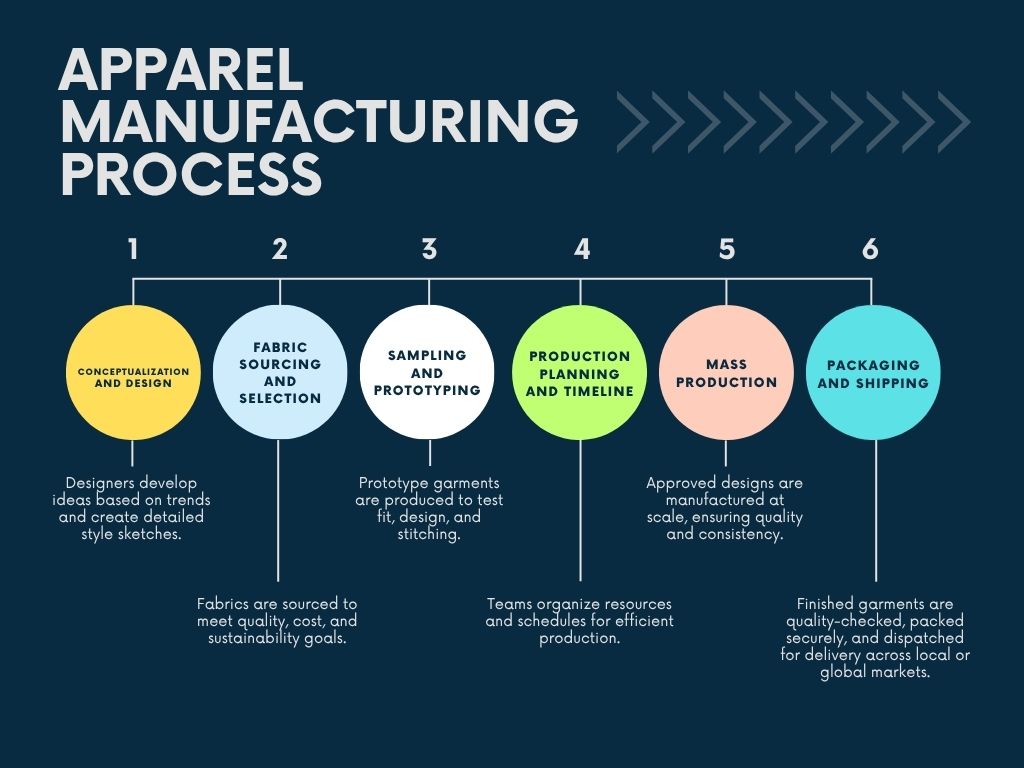
1. Conceptualization and Design
First, any piece of clothing originates from an idea. Designers create various styles inspired by market trends or the season’s identity. They work on sketches, materials, color and design details to create a clear vision of what they want to achieve.
2. Fabric Sourcing and Selection
The process continues with the fabric manufacturer. According to the design, the teams must search for raw materials in the market that meet the quality, cost, and sustainability parameters. When it comes to brands that have trusted their manufacturing operations with apparel vendors in USA, local sourcing can help speed up this stage significantly.
3. Sampling and Prototyping
Before mass production, samples are created. These prototypes enable designers to view the garment in 3D or physical samples, test the fit / stitching, and make any necessary adjustments. Sampling is crucial in the garment manufacturing process because it ensures that final products match the intended design perfectly.
4. Production Planning and Timeline
Post sample approval, the focus is now on apparel production planning. This stage involves developing the production sequence, securing resources, and coordinating with various teams, from the cutting section to the sewing / finishing and packing team, to meet deadlines.
5. Mass Production
Once pre-production activities are completed, massive production begins. Hundreds to thousands of garments are cut, sewn, and assembled according to the requirements. Factories in the US and abroad have work orders that guide them every step of the way, thus ensuring consistency.
6. Packaging and Shipping
The final products receive detailed attention as they are checked, packed, and prepared for delivery. Whether being sent to boutiques or being it bulk orders going to other parts of the world, this last stage of the clothing production path is due to logistics.
Workflow of the Apparel Production Process
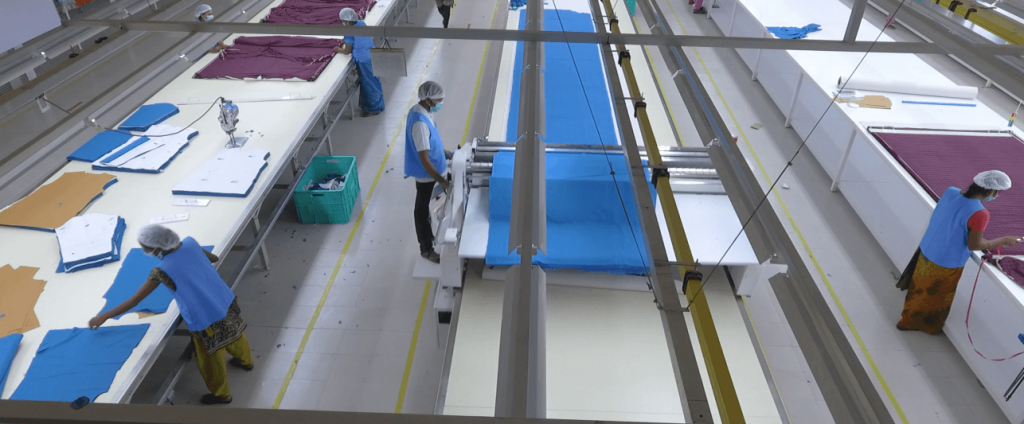

Understanding the workflow of the apparel manufacturing process gives designers a clear demonstration of the initial idea development to the final product manufacturing stages:
- Designing: The inventive inputs are turned into digital or paper sketches.
- Pattern Making: Technical patterns are drawn to assist in cutting fabric and making clothes.
- Cutting: The fabric is precisely cut as per pattern templates to save the fabric and reduce waste to a minimum.
- Sewing: Cut pieces are stitched together either by skilled workers or automated machines to give a new garment shape.
- Finishing: Adding buttons, labels, finishing embroidery, or washes are some of the finishing touches.
- Quality Check: An inspection process is performed to ensure that the garment corresponds to the design and has the appropriate quality.
Without the coordination between the departments, the whole process would not be possible. At some large apparel manufacturers in the USA, the digital platform-enhanced communication channels between design, sourcing, production, and shipping teams are heavily relied on. The reason is that these channels of communication are the key to decreasing errors and increasing the speed of the entire manufacturing process.
Different Types of Apparel Manufacturing Processes
1. Section Production System
Regarding this procedure, the work can be divided into different segments according to the type of equipment. So, for example, the machines that make the collar are together in one place while those that make the sleeves are located in another area. This setup ensures that the flow will be efficient, the transitions between the stages will be smooth, and excellent quality products will be made.
2. Progressive Bundle System
In this system, workers are assigned specific tasks in a sequential flow. Garments are bundled in parts and passed along to each operator who performs their specialized task, creating a smooth, efficient production cycle. This method ensures consistency and efficiency, making it popular with large-scale manufacturers.
3. One-piece Flow System
Contrary to progressive bundles, the one-piece flow method features one garment part passing through each workstation at a time. As a result, the production time is cut down, and the system’s efficiency is improved. Hence, it is more suitable for the business environment with faster response requirements and versatile production.
4. Modular Production System
Here, a team of multi-skilled workers collaborates to produce garments, performing various tasks modularly. This system emphasizes teamwork and flexibility, and each team is responsible for the quality and speed of production, fostering a sense of shared responsibility.
5. Make-through System
In the make-through process, a single tailor manages the entire garment creation process from start to finish. This approach gives the worker complete control, ensuring a consistent product with a personal touch, making it ideal for bespoke or high-end clothing lines.
6. Overhead Production System (OPS)
The OPS system involves hanging garment pieces on overhead rails, allowing the workstations to process individual parts. This system is often used for streamlined, efficient production where garment components are easily moved through the stages with minimal handling.
Main Methods of Apparel Manufacturing
There are also different main methods of apparel manufacturing, which include:
- Assembly Line Production: High efficiency, where each worker specializes in one task.
- Modular Production System: Small teams work on completing entire garments, promoting flexibility.
- Lean Manufacturing: Focused on reducing waste and increasing efficiency, widely adopted by modern USA apparel manufacturers.
Choosing the right method depends on your brand’s needs, order volume, and turnaround expectations.
Quality Control in Apparel Manufacturing

Quality is non-negotiable. Throughout the apparel manufacturing process, strict quality control measures are in place, including:
- Fabric Inspection: Checking for color consistency, weaving defects, or shrinkage.
- In-Process Inspection: Monitoring cutting, stitching, and finishing steps. In addition, garment testing has to be done prior to shipping goods
- Final Inspection: Ensuring garments meet specifications before packaging.
Common quality parameters include seam strength, color fastness, fabric weight, and garment measurements.
Brands that partner with reputable apparel vendors often experience fewer returns and higher customer satisfaction rates, underscoring the importance of quality control.
Technologies Used in Apparel Manufacturing
The rise of technology has revolutionized the apparel production landscape:
- CAD Software for digital design and pattern making.
- 3D Virtual Sampling to reduce the need for physical prototypes.
- Automatic Cutting Machines for precision fabric cutting.
- ERP Systems for streamlining apparel production planning and inventory management.
Smart technologies make it possible for apparel manufacturers in USA and globally to produce faster, with higher accuracy and less waste.
The Role of Automation in Apparel Manufacturing
Automation is not about replacing humans; instead, it empowers humans to focus on other major parts of their work. From robots capable of sewing on a large scale to artificial intelligence-based inspection devices that check the quality of the fabric, automation consolidates mundane routines, minimizes errors, and enables the workforce to focus on tasks of the highest value.
Automation is the best way to keep the production of clothes on a large scale competitive without a loss of quality. Through the application of automation, leading apparel vendors facilitate the reduction in the number of working days and an increase in efficiency.
Delivery and Logistics
After production, the products are shipped to distribution centers, retailers, or directly to customers. Smooth logistics ensure that the new season’s collections arrive at shops on schedule, making it feasible for the goods to be sold at top prices.
Working with trustworthy apparel vendors in the USA streamlines the logistics process, enables faster delivery times, and enhances information flow within the supply chain.
Pearl Global: A Global Apparel Vendor with Strategic USA Operations
Pearl Global is one of the leading clothing vendors serving fashion brands across the globe. As a vertically integrated apparel manufacturer, the company operates through a robust international supply chain. While all the apparel manufacturing takes place in countries like Vietnam, Indonesia, Guatemala, Bangladesh, and India, the sales and design headquarters are based in the USA. This U.S.-based team plays a pivotal role in overseeing operations, coordinating product development, and ensuring that global production units meet high standards of design integrity, quality, and delivery timelines.
By integrating digital design platforms, ERP systems, and advanced quality control mechanisms, Pearl Global ensures its production units follow strict compliance, sustainability, and operational efficiency standards. The U.S. teams also monitor vendor performance across global manufacturing locations, enabling real-time communication and quick response to fashion trends or client needs. This hybrid model—local oversight combined with international production—exemplifies how modern clothing vendors in the USA can offer scalable, fast, and reliable apparel solutions while optimizing cost and efficiency across continents.
Conclusion
The apparel manufacturing process is a blend of creativity, precision, technology, and craftsmanship. At every step, from the initial drawing to the final delivery, each person does essential work that shapes our everyday clothes.
Whether you are a startup brand that exclusively sources from US apparel manufacturers or a distinguished label collaborating with international apparel vendors, grasping the entire process of the garment manufacturing cycle means you are well-connected, efficient, and aware of human rights.
By appreciating the depth and detail behind apparel production, we not only make better business decisions, we also contribute to the sustainable and innovative transformation of the fashion industry.